Archives
- 2026-03
- 2026-02
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2019-05
- 2019-04
- 2018-11
- 2018-10
- 2018-07
-
In a report from the UK an outbreak of W
2019-04-29
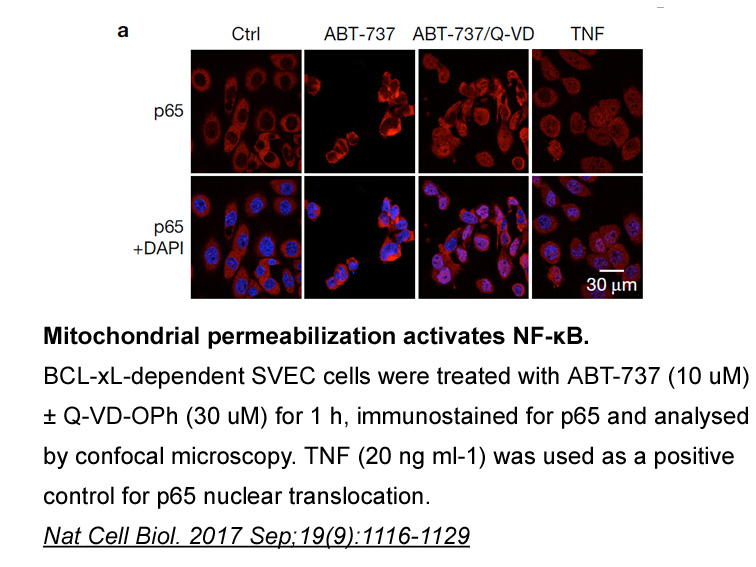
In a report from the UK, an outbreak of W135 was observed between July, 2015, and January, 2016, in 15 adolescents who order latrunculin a did not have any direct epidemiological, temporal, or spatial links. All these patients presented predominantly with gastrointestinal symptoms. A clinical diagno
-
br I agree with Hemant Ojha and Sampanna Jung
2019-04-29
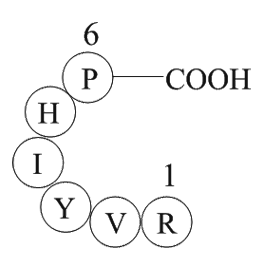
I agree with Hemant Ojha and Sampanna Jung Rayamajhi that, although the suggestion to use doxycycline for treatment of a presumptive diagnosis of scrub typhus is justified, we clearly have to be on the lookout for doxycycline-resistant scrub typhus. Indeed, the Comment was written in an attempt to
-
The low coverage achieved in
2019-04-29
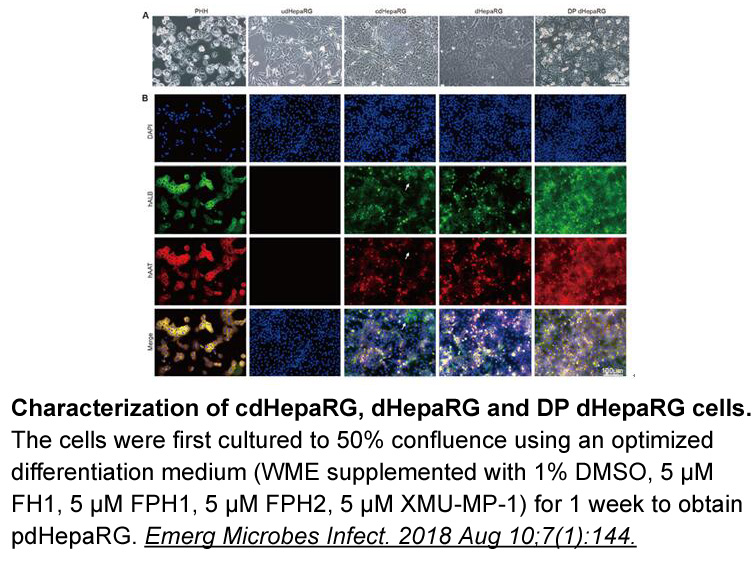
The low coverage achieved in this study is another major concern. High coverage promotes equity, and evidence shows that rapid increases in coverage of maternal and child health interventions bring about gains in equity. Greenland and colleagues compare clusters with high exposure and low exposure,
-
Increasing the duration of PVAB might be an
2019-04-29
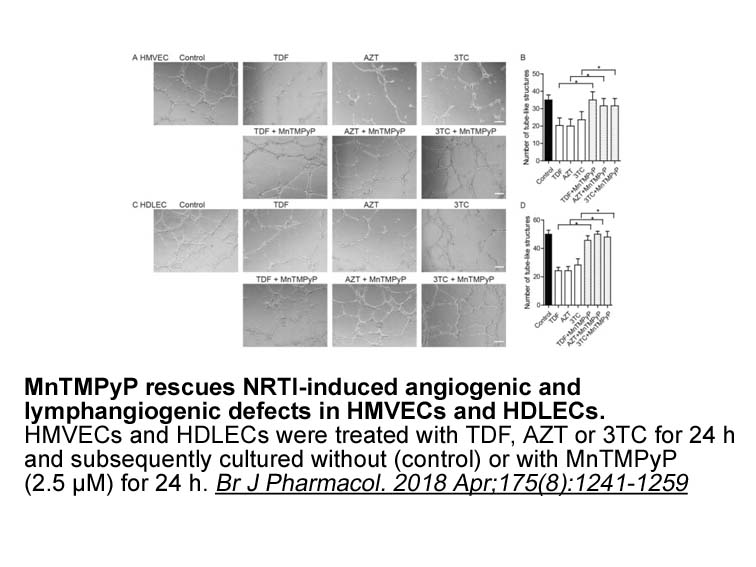
Increasing the duration of PVAB might be an effective means of preventing FFRW oversensing in the atrial channel. However, this narrows the search window of atrial sensing, and shortens the window of ATA detection, which might decrease the likelihood of detecting ATA. Conversely, a short PVAB widens
-
Introduction Atrial fibrillation AF is
2019-04-29
Introduction Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia managed in clinical practice and the most common arrhythmia requiring hospitalization [1,2]. Thromboembolism occurs with similar incidence, regardless of the form of AF [3,4]. AF management includes anticoagulation to preve
-
ERS and BrS are thought to represent
2019-04-29
ERS and BrS are thought to represent 2 manifestations of the JWSs. Both syndromes are associated with vulnerability to development of polymorphic VT and VF leading to SCD [1–3,15] in young adults with no apparent structural somatostatin receptor disease and occasionally to sudden infant death syndr
-
En la obra de Cuadra una familia campesina confronta
2019-04-29
En la obra de Cuadra, una familia campesina confronta trágicamente la guerra civil entre conservadores y liberales. Víctimas pasivas de las élites y no actores políticos, estos campesinos ven cómo los principios familiares tradicionales y del minifundio son desarticulados por la guerra y el abuso de
-
LY2584702 En otros instrumentos legales se
2019-04-29
En otros instrumentos legales se manifiesta la intención de fortalecer el principio de no dañar. Brasil es el que aborda con mayor profundidad este principio, debido LY2584702 su extensión territorial, y la responsabilidad que surge en la gestión y uso del recurso agua, relacionado por ejemplo con e
-
El pnsd entend a al poder nacional como
2019-04-29
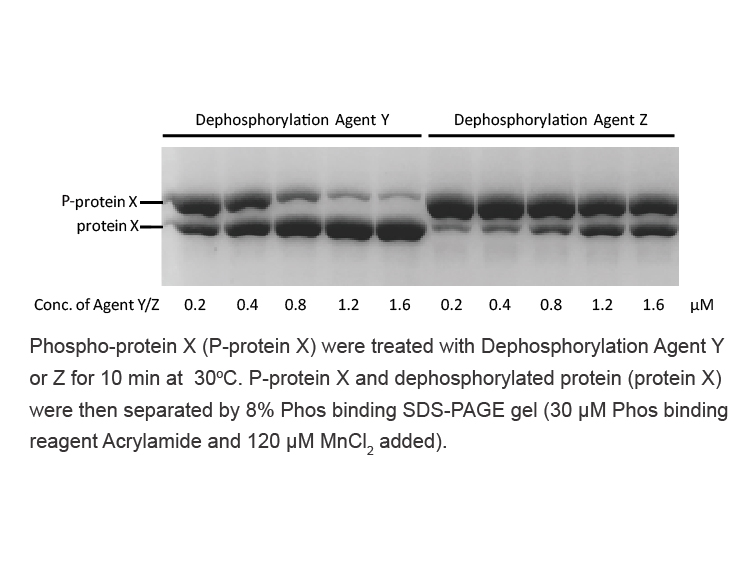
El pnsd entendía al poder nacional como la unión del poder militar, político, económico y social. Ahora sí, todos los campos se orientaban cytoskeleton combatir la “subversión”. Si los tres primeros requerían de los aparatos materiales del Estado, el último movilizaba los aparatos ideológicos de la
-
4-ethylphenyl sulfate O conhecimento dos autores brasileiros
2019-04-29
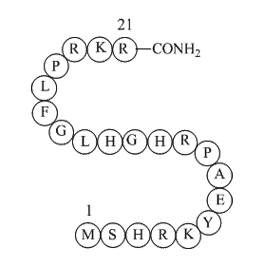
O conhecimento dos autores brasileiros tanto na Argentina como no México e dos autores latino-americanos no Brasil foi sustentado no século 20 em grande medida pelo fomento diplomático e não pelo mercado. Trocas regidas pelo interesse mútuo de autores dos países latino-americanos —e basta um olhar a
-
A year old male with a past medical history of
2019-04-29
A 30-year-old male with a past medical history of adult-onset Still׳s disease diagnosed 1.5 years ago was transferred from an outside hospital with fever, jaundice, weight loss, and impending respiratory failure. On physical exam, there was splenomegaly and imaging demonstrated retroperitoneal lymph
-
br Introduction Since China has become the world s second
2019-04-28

Introduction Since 2010, China has become the world’s second largest economy. The middle-class population has been increasing dramatically in China’s big cities, whereas the majority of rural residents remain financially impoverished. The average income of Chinese farmers is one-fourth of that ma
-
We have developed a novel
2019-04-28
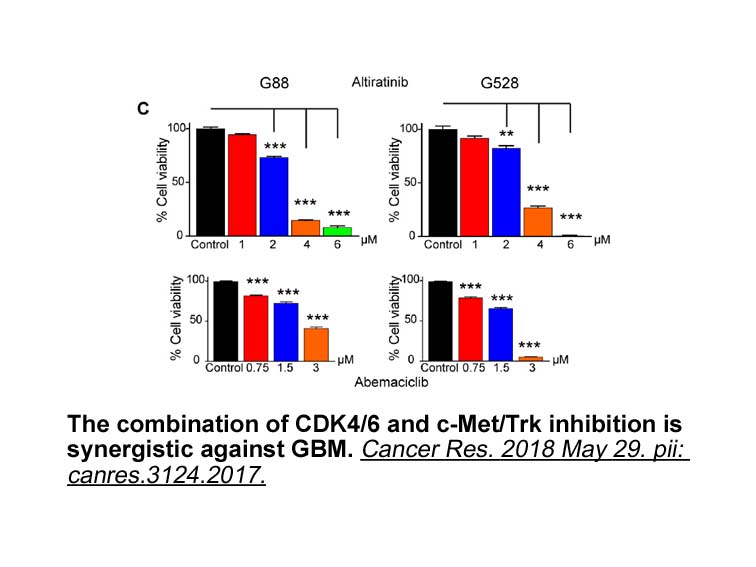
We have developed a novel radioimmunotherapy (RIT) strategy targeting CD123 overexpressed on LSCs that we are evaluating in the NOD/SCID mouse AML model. Indium-111 (111In) labeled to CSL360 (CSL Limited, Parkville, Australia), a chimeric IgG1 specific for CD123, was used to deliver Auger electron i
-
The time to use the distraction
2019-04-28

The time to use the distraction–osteogenesis apparatus in children was suggested to be after infection eradication. We used the Ilizarov apparatus immediately following radical debridement to provide stability and prepare for distraction–compression osteogenesis 1 week later. Circular external fixa
-
br Entrainment As the principles of entrainment initially de
2019-04-28

Entrainment As the principles of entrainment initially described by Waldo for atrial flutter could be fulfilled by scar-mediated VT, characterization of the reentrant circuit provided a central isthmus as a favorable target [33,34]. In the late 1980s, the collective descriptions of entrainment, o
15990 records 1034/1066 page Previous Next First page 上5页 10311032103310341035 下5页 Last page